What is 3G technology?
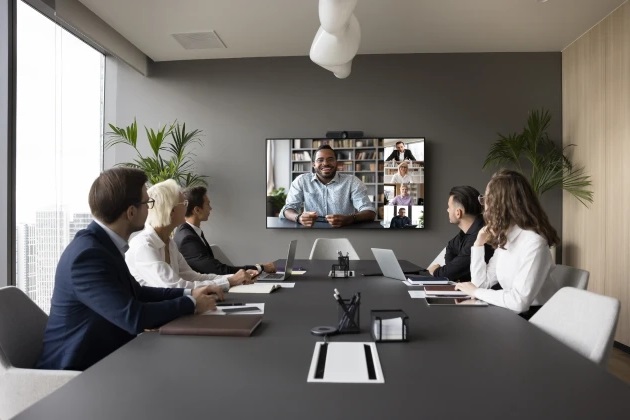
In mobile communications, the technology developed based on the 2G GSM architecture is called 3G (third generation) technology. Currently, the four major 3G standards in the world are WCDMA, CDMA2000 (USA), TD-SCDMA and WiMAX.
When GSM was developed, data transmission was not a major consideration and it was initially used primarily for voice communications, so GSM has slower data transmission speeds. In contrast, 3G technology has significantly improved compared to GSM, with a higher frequency range, usually between 1.8GHz and 2.5GHz, providing higher data transmission rates and better voice quality. Supporting a wider range of multimedia and data services can better meet the needs of mobile Internet access, although high-definition video playback may still encounter performance bottlenecks.
The introduction of 3G technology supports higher throughput and data transmission speeds, making seamless roaming possible around the world. This generation of technology enables users to browse the Internet more efficiently, stream video and send multimedia messages, and paves the way for new uses such as GPS navigation, mobile TV and video calling. At the same time, 3G technology also needs to consider good compatibility with existing second-generation systems.
In order to realize these services, the wireless network must support different data transmission rates to ensure stability in different environments, including at least 2Mbps (megabits per second) in indoor environments and 384kbps (kilobits per second) in outdoor environments. , and it needs to support a speed of at least 144kbps when driving (the actual value may vary depending on the network environment).
What are the main differences between 2G and 3G technologies?
1. Frequency range: In the United States, the 2G frequency range is mainly in the 850 MHz and 1900 MHz bands. The 3G frequency range CDMA2000 is mainly in the 850 MHz and 1900 MHz frequency bands, while WCDMA is mainly in the 1700 MHz (AWS frequency band) and 2100 MHz frequency bands.
2. Data transfer: 3G networks offer faster download speeds and faster access to data and applications than 2G networks. Data transfer speeds in 2G networks are less than 50,000 bits per second, while data transfer speeds in 3G networks are well above 4 million bits per second.
3. Service type: 2G mainly focuses on voice communication and supports text messages (SMS) and simple data services, while 3G supports more complex multimedia and Internet services on this basis.
4. Roaming capability: 2G roaming capability is limited and mainly relies on the coverage of the same network. 3G provides a better seamless roaming experience and makes international mobile communications more convenient for users.
5. Security measures: 3G technology is also better than 2G technology in terms of security. 3G networks introduce more advanced encryption and authentication measures to ensure users are more secure when communicating with other devices.
3G cell phone scrambler:
The impact of 3G technology has increased the demand for mobile communications, and the means of spying on privacy have become more diverse. Therefore, we have launched a 3G jammer to block unauthorized communications and meet your security needs.
Cell Phone Jammer:
Searched By Frequencyband:
Showing all 7 results
- 337.45$
Designed for high-intensity and long-term use, this GSM signal jammer for cell phones can achieve continuous 7×24 hours of uninterrupted operation. It supports dual-mode power supply for vehicle and indoor use, plug and play, and is suitable for a variety of scenarios.
- 249.36$ – 305.79$
Portable 5 bands car-mounted GSM 3G cell portable jammer , 3W output power, a jamming range of up to 20m, and the ability to jam multiple frequencies. The built-in quiet cooling fan ensures that the device can be used in a low profile manner without attracting attention, which is especially important in sensitive environments that require careful handling.
- 167.46$
When the GSM cell phone radio jammers starts working, it intercepts 2G and 3G network signals on mobile devices by emitting radio waves and generating white noise, blocking unauthorized mobile data transmission within a range of 20 meters.
- 289.16$
The emergence of innovative solutions such as the 4 antennas electronic device frequency blockers not only do these devices stand out with their gold design, but they also provide a reliable way to prevent the transmission of specific frequency signals such as 2G, 3G, and GPS.
- 269.86$
Unlock the power of protection with our top-of-the-line mobile cell scrambler featuring 5 versatile frequency bands. Not just a blocker, this innovative gadget doubles up as a practical power bank, adding even more value to your daily usage.
- 352.69$
This first-rate desktop cell phone jamming device introduces an affordable solution in the world of signal security, providing specialized jamming capabilities for mobile networks. With a focus on affordability and efficiency, this device stands out for its cost-effective performance.
- 443.19$
Looking for top-tier privacy and data security? Look no further! Introducing our GSM jamming devices! With a range of up to 50 meters, we clear out irrelevant signals, safeguarding your data like never before!
Showing all 7 results